
April Issue, 2016
Urinary Tract Infections in Adults
 The urinary tract
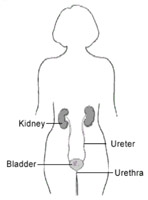
The urinary tract
Infections of the urinary tract are the second most common type of infection in the body. Women are especially prone to UTIs as one woman in five develops a UTI during her lifetime. UTIs in men are not as common as in women but can be very serious when they do occur.
The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The kidneys remove excess liquid and wastes from the blood in the form of urine, narrow tubes called ureters carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder, a sack-like organ in the lower abdomen. Urine is stored in the bladder and emptied through the urethra.
What are the causes of UTI?
Normally, urine is sterile, as the urinary system is structured in way that helps ward off infection. An infection occurs when tiny organisms, usually bacteria from the digestive tract, cling to the opening of the urethra and begin to multiply. Most infections arise from one type of bacteria, Escherichia coli (E. coli), which normally lives in the colon.
Who is at risk?
- Any abnormality of the urinary tract that obstructs the flow of urine (a kidney stone or enlarged prostate gland, for example)
- Urinary incontinence, catheters, or tubes, placed in the urethra and bladder.
- Any illness (e.g. diabetes) or medication that suppresses the immune system.
- Sexual activity, use of spermicidal foam, also tend to have growth of E. coli bacteria in the vagina.
- Previous UTI
- Advanced age : Older adults are more likely to get UTIs
What are the symptoms of UTI?
1. Frequent urge to urinate & a painful, burning, feeling in the area of the bladder or urethra during urination.
2. It is not unusual to feel bad all over, tired & weak and to feel pain even when not urinating.
3. Often women feel an uncomfortable pressure above the pubic bone, and some men experience fullness in the rectum.
4. It is common for a person with a urinary infection to complain that, despite the urgency, only a small amount of urine is passed. The urine may look milky, cloudy, or reddish.
5. Normally, a UTI does not cause fever if it is in the bladder or urethra. A fever may mean that the infection has reached the kidneys. Other symptoms of a kidney infection include pain in the back or side below the ribs, nausea, &/or vomiting.
6. There are other disorders of the bladder that may cause bladder pain, or painful urination. The first step is to keep a diary of symptoms, avoid bladder irritants (carbonated beverages, caffeine, citrus, & nicotine) and see your doctor; self- diagnosing a UTI based on symptoms alone leads to inappropriate use of antibiotics.
How are UTI diagnosed?
You will be asked to give a "clean catch" urine sample by washing the genital area and collecting a "midstream" sample of urine in a sterile container to test for pus and bacteria. This method of collecting urine helps prevent bacteria around the genital area from getting into the sample and confusing the test results. Initial testing will take place in the Dr's office, and then sent to the lab for further analysis. If bacteria are present, they are tested against different antibiotics to see which drug best destroys the bacteria. When an infection does not clear or you have recurrent infections, imaging studies may be ordered to determine if your urinary system is normal.
How are UTI treated?
UTIs are treated with antibiotics. The choice of drug and length of treatment depend on the patient's history and the urine tests that identify the offending bacteria. Often, a UTI can be cured with 1 or 2 days of treatment if the infection is not complicated by an obstruction or other disorder. Regardless of the length of prescribed treatment, is important to take the full course of treatment because symptoms may disappear before the infection is fully cleared. Additional measures include: drinking plenty of water to help cleanse the urinary tract of bacteria and avoid coffee, nicotine, and spicy foods, analgesics for comfort.
How are UTIs prevented?
1. Drink plenty of water every day. Some doctors suggest drinking cranberry juice.
2. Urinate when you feel the need; don't resist the urge to urinate.
3. Wipe from front to back to prevent bacteria from the anus from entering the vagina or urethra.
4. Take showers instead of tub baths.
5. Cleanse the genital area before sexual intercourse.
6. Avoid using feminine hygiene sprays and scented douches, which may irritate the urethra.
7. Research shows that components found in cranberry may prevent bacteria, such as E. coli, from clinging to the cells along the walls of the urinary tract and causing infection. Cranberry can be taken alone or in combination with vitamin C.
Infections in Men
UTIs in men are often a result of an obstruction—for example, a urinary stone or enlarged prostate—or from a medical procedure involving a catheter. The first step is to identify the infecting organism and the drugs to which it is sensitive. Usually, doctors recommend lengthier therapy in men than in women, in part to prevent infections of the prostate gland.
For More Information
American Urological Association
1000 Corporate Boulevard
Linthicum, MD 21090
Phone: 1–866 (746–4282) Fax: 410–689–3800
Internet: www.urologyhealth.org
National Kidney & Urological Diseases Info
3 Information Way
Bethesda, MD. 20892-3580
Phone: 1–800–891–5390 FAX 703-738-4929
Internet: www.kidney.niddk.nih.gov
Connect


